Local climate zone classification using a multi-scale, multi-level attention network
 Local climate zone classification using MSMLSA
Local climate zone classification using MSMLSAAbstract
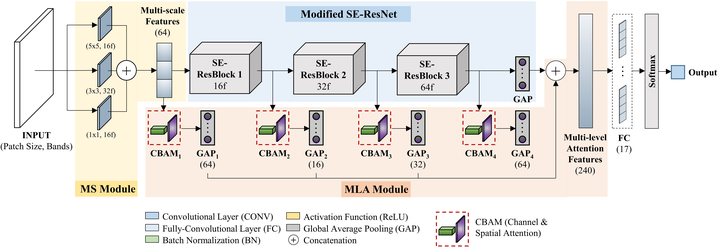
Local Climate Zones (LCZ) offer a climate-aware and standardized classification scheme composed of 17 urban and natural landscape classes. Recent deep learning-based LCZ classification studies have adopted a scene classification approach with computer vision-inspired models. In light of these advancements, this study introduces a multi-scale, multi-level attention network (MSMLA-Net) for deep learning-based LCZ classification. MSMLA-Net integrates a multi-scale (MS) module to generate multi-scale features from the input data and a novel multi-level attention (MLA) module as a branch unit from the model’s main ResNet backbone. MLA uses the convolutional block attention module (CBAM) at multiple stages to generate multi-level spatially and spectrally enhanced features for context aggregation. This study presents comprehensive model-based experiments on model depth, the individual and combined influence of MS and MLA modules, and the addition of attention mechanisms. Furthermore, data-based experiments are conducted to determine optimal Sentinel-2 spectral bands, while OpenStreetMap (OSM) building data, ALOS World 3D DSM height information, and a national land cover map are included as ancillary bands. LCZ classification tests are conducted on six major cities in South Korea. With regards to model-based performance, MSMLA-Net was built using a modified SE-ResNet50 backbone (MSMLA-50) and obtained the best classification results using 48 by 48-pixel input patches with a combination of all Sentinel-2 and ancillary bands, outperforming three state-of-the-art LCZ classification models. In particular, only MSMLA-50 reached over 70% built-up overall accuracy and maintained high accuracy even when tested on completely unseen areas in a “citywise” leave-one-out sampling strategy. For data-based results, the combination of Sentinel-2 Red Edge bands were helpful, mainly due to the greater number of available bands. Training only ancillary data generated up to 75.0% for built-up overall accuracy, albeit at the cost of low natural overall accuracy. Using all available bands and ancillary data produced the best results, but a combination of only OSM and Sentinel-2 bands also generated comparable accuracy. Ultimately, the proposed MSMLA-Net bridges advanced computer vision techniques such as attention mechanisms and multi-level context aggregation to improve LCZ classification. The MS and MLA modules can be applied on different backbones, sophisticated sampling schemes, and data inputs to flexibly achieve improved classification results.